Oleh: Yustin Nur Faizah, S.Tr.,Ak.,M.Ak.,AK.
Introduction
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a crucial framework for organizations to identify, assess, and manage risks that could hinder their objectives (Otero González et al., 2020). In the context of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), ERM plays a vital role in aligning business strategies with global sustainability targets (Shah et al., 2022). The SDGs, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, provide a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future (Allen et al., 2018). Integrating ERM with the SDGs ensures that organizations not only mitigate risks but also contribute positively to sustainable development.
Understanding Enterprise Risk Management
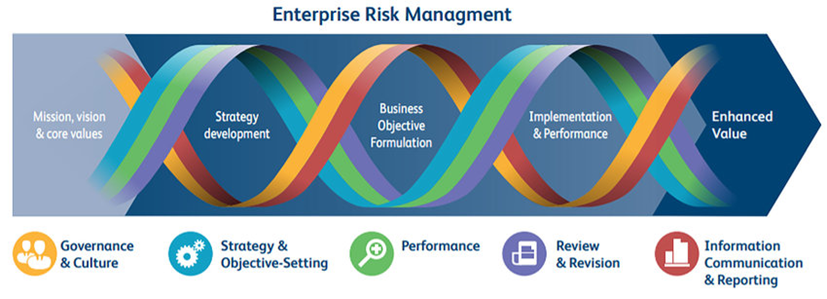
According COSO,( 2004) ERM is a structured and continuous process that organizations use to manage risks across all areas of their operations. The key components of ERM include:
- Risk Identification: Recognizing potential risks that could affect the achievement of objectives.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing strategies to minimize the impact of risks.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuously tracking risks and the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
- Risk Reporting: Communicating risk information to stakeholders.
ERM helps organizations anticipate uncertainties and prepare for various scenarios, making it an essential tool for achieving long-term goals.
The Sustainable Development Goals
The SDGs consist of 17 goals and 169 targets designed to address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice(Campagnolo et al., 2016). These goals are:
- No Poverty
- Zero Hunger
- Good Health and Well-being
- Quality Education
- Gender Equality
- Clean Water and Sanitation
- Affordable and Clean Energy
- Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Reduced Inequality
- Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Responsible Consumption and Production
- Climate Action
- Life Below Water
- Life on Land
- Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- Partnerships for the Goals
Organizations play a critical role in achieving these goals through responsible practices and innovative solutions.
Integrating ERM with the SDGs
According (Febrianti & Novita, 2021) Integrating ERM with the SDGs involves aligning risk management practices with sustainable development objectives. This integration offers several benefits:
- Strategic Alignment: ERM helps organizations align their strategies with the SDGs, ensuring that business activities contribute to global sustainability efforts.
- Enhanced Risk Awareness: By considering SDG-related risks, organizations become more aware of potential social, environmental, and economic impacts, leading to more comprehensive risk assessments.
- Improved Decision-Making: Integrating the SDGs into ERM frameworks supports informed decision-making that balances risk and opportunity in the context of sustainability.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Addressing SDG-related risks and opportunities can enhance stakeholder trust and engagement, as stakeholders increasingly value sustainability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations that incorporate the SDGs into their ERM processes are better positioned to comply with evolving regulations and standards related to sustainability.
Practical Steps for Integration
- Mapping SDGs to Organizational Objectives: Identify which SDGs are most relevant to the organization’s mission and operations. This helps in focusing efforts on areas with the highest impact.
- Risk Identification and Assessment: Incorporate SDG-related risks into the ERM process. This includes assessing risks such as climate change, resource scarcity, social inequality, and regulatory changes.
- Developing Mitigation Strategies: Create strategies to mitigate SDG-related risks. For example, reducing carbon emissions, promoting diversity and inclusion, and ensuring ethical supply chains.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Implement mechanisms to monitor progress towards SDG targets and report on sustainability performance. This fosters transparency and accountability.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update the ERM framework to reflect changing circumstances and emerging risks related to the SDGs.
Case Studies
- Unilever: Unilever has integrated ERM with its sustainability strategy, focusing on areas such as climate action, responsible consumption, and inclusive growth. By aligning its risk management practices with the SDGs, Unilever has improved resilience and achieved significant sustainability milestones.
- Patagonia: Patagonia, an outdoor apparel company, emphasizes environmental sustainability in its ERM approach. The company addresses risks related to climate change and resource depletion, aligning its operations with SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Conclusion
Integrating Enterprise Risk Management with the Sustainable Development Goals is a strategic approach that enables organizations to manage risks while contributing to global sustainability efforts. By aligning risk management practices with the SDGs, organizations can enhance resilience, improve stakeholder relations, and support the achievement of a sustainable and prosperous future for all.
References
Allen, C., Metternicht, G., & Wiedmann, T. (2018). Initial progress in implementing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): a review of evidence from countries. Sustainability Science, 13(5), 1453–1467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0572-3
Campagnolo, L., Carraro, C., Eboli, F., & Farnia, L. L. (2016). Assessing SDGs: A New Methodology to Measure Sustainability. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2715991
COSO. (2004). Enterprise Risk Management — Integrated Framework Executive Summary. New York, 3(September), 1–16. http://www.coso.org/documents/COSO_ERM_ExecutiveSummary.pdf
Febrianti, I., & Novita, N. (2021). COSO’s Enterprise Risk Management Framework in Agriculture Startup to Support the Achievement of SDGs Pillars. TIJAB (The International Journal of Applied Business), 5(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.20473/tijab.V5.I1.2021.18-36
Otero González, L., Durán Santomil, P., & Tamayo Herrera, A. (2020). The effect of Enterprise Risk Management on the risk and the performance of Spanish listed companies. European Research on Management and Business Economics, 26(3), 111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iedeen.2020.08.002
Shah, S. Q. A., Lai, F.-W., Shad, M. K., & Jan, A. A. (2022). Developing a Green Governance Framework for the Performance Enhancement of the Oil and Gas Industry. Sustainability, 14(7), 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14073735
